The Two Vector Functions (V and U) computes the resulting function, vector (W) or scalar, that is the result of the operation and 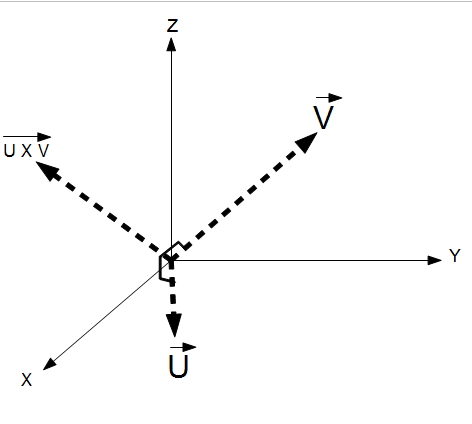 two vectors (V and U) in three dimensional space.
two vectors (V and U) in three dimensional space.
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following:
- (V): Enter the x, y and z components of V
- (U): Enter the x, y and z components of U
- OPERATION: VxU, V+U, V-U, V*U,angle-between
Vector Function (W): The calculator returns the result of the specified operation.
The Math / Science
The cross product of two vectors create a third vector that is orthogonal (90 degrees) from both original vectors. This is know as a normal vector to the plane created by vectors U and V. For this reason, a single normal vector is often used to define a plane. To compute the cross product of two vectors, compute the determinant of the following:
| i j k |
V x U = |Vx Vy Vz|
|Ux Uy Uz|
V x U = (Vy⋅ Uz - Uy⋅ Vz), -1(Vx ⋅ Uz - Ux ⋅ Vz), (Vx ⋅ Uy - Ux⋅Vy)
3D Vector Functions
 k⋅V - scalar multiplication
k⋅V - scalar multiplication- V/k - scalar division
- V / |V| - Computes the Unit Vector
- |V| - Computes the magnitude of a vector
- U + V - Vector addition
- U - V - Vector subtraction
- |U - V| - Distance between vector endpoints.
- |U + V| - Magnitude of vector sum.
- V • U - Computes the dot product of two vectors
- V x U - Computes the cross product of two vectors
- V x U • W - Computes the mixed product of three vectors
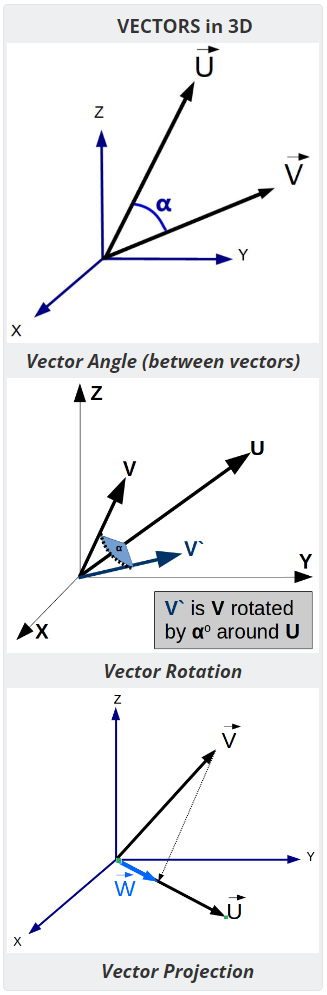
- Vector Angle - Computes the angle between two vectors
- Vector Area - Computes the area between two vectors
- Vector Projection - Compute the vector projection of V onto U.
- Vector Rotation - Compute the result vector after rotating around an axis.
- Vector Components 3D - Returns a vector's magnitude, unit vector, spherical coordinates, cylindrical coordinates and angle from each axis.
- (ρ, θ, φ) to (x,y,z) - Spherical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (ρ, θ, φ) - Cartesian to Spherical coordinates
- (r, θ, z) to (x,y,z) - Cylindrical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (r, θ, z) - Cartesian to Cylindrical coordinates
- (x,y) to (r, θ) - Cartesian to Polar
- (r, θ) to (x,y) - Polar to Cartesian
- Vector Normal to a Plane Defined by Three Points
