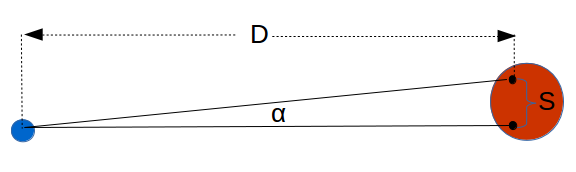
The Astronomical Distance (SAF) calculator uses the small angle formula (SAF) to compute the distance to an astronomical body based on the size of the object or separation between two objects (S) and the angle subtended (α).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (S) Separation (see diagram).
- (α) Angle Subtended.
Distance (D): The calculator returns the distance in Astronomical Units (ua). However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units (e.g. light-years) via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
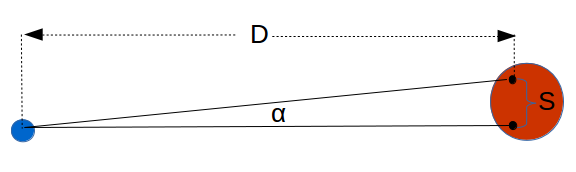
Use the small angle formula (SAF) to compute the distance given the size and angle subtended.
D = S / α
where:
- D is the Small Angle Formula Distance to the object.
- S is the size of the object.
- α is the angle subtended.
This is an essential step in computing distance with the parallax method. Note: some textbooks show this formula with a coefficient of 2.06 x 105. This is the equivalent to the formula used here, because vCalc makes the appropriate unit conversions from arc-seconds to radians and does not require the 2.06 x 105 coefficient.
Astronomical Units
Because of the enormity of space and the size of the objects studied, the field of astronomy employs units not commonly used in everyday life. Nonetheless, these units do translate into common units at a grand scale, and vCalc provides automatic conversions between units for calculator inputs and answers via the pull-down menus. The following is a brief description on the distance, mass and time units employed in the field of astronomy
Astronomy Distance Units
Astronomical Unit (au): Within our solar system, a common measure of distance is au, which stands for astronomical units. A single astronomical unit is the mean distance from the Sun's center to the center of the Earth.
| Astronomical Unit (au) | Distance from Sun (au) |
|---|---|
|
|
Light Travel in Time: Light is a primary observable when studying celestial bodies. For this reason, the distance to these objects are measured in the amount of time it would take light to travel from there to the Earth. We can say that an object is one light-year away, and that means that the object is at a distance where it took an entire year for light from the object to travel to Earth. Since the speed of light is 299,792,458.0 meters per second, one can compute the distance equal to a light year as follows:
1 light year = 299,792,458.0 (meters / second) x 31,536,000 (seconds / year) = 9,460,528,405,000,000 meters
The same exercise can be used for light traveling shorter periods of times, light seconds, light minutes, light hours and light days. Since even these units are not enough when computing distances across the universe, there is also a light relative distance of kilo-light years (1000 light years), or the distance light travels in a thousand years!
| Light Second | Light Minute | Light Hour | Light Day | Light Year | Kilo-Light Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
299,786 km 186,278 miles 0.002 au |
17,987,163 km 11,176,705 miles 0.12023 au |
1,079,229,797 km 670,602,305 miles 7.214 au |
25,901,515,140 km 16,094,455,343 miles 173.14 au |
9,460,528,405,000 km 5,878,499,814,210 miles 63,240 au 0.306 parsecs |
9,460,528,405,000,000 km 5,878,499,814,210,000 miles 63,240,000 au 306 parsecs |
Angle Shift Seen from Earth: Because the Earth goes around the Sun, our observation of distant objects such as stars results in an angular shift when observed at opposite sides of the elliptical orbit. This shift is used as the basis of a unit knows as a parsec. A parsec was traditionally defined as the distance where one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arcsecond. A parsec was redefined in 2015 to 648000/π astronomical units. Proxima Centauri, is the nearest star to the Sun and is approximately 1.3 parsecs (4.2 light-years) from the Sun. A mega-parsec is a million parsecs.
| Parsec | Mega-parsec |
|---|---|
|
|
Astronomy Mass Units
Astronomical units also apply to the mass of enormous objects such as moons, planets and stars. For this reason, astronomy also employs mass units that compare other objects to ones familiar to us. For example, stars are often measured in mass units of solar masses. This is a comparison of their mass to the mass of our sun (one solar_mass). For planets, astronomers use Earth masses and Jupiter masses for understanding the relative size of rocky planets and gas giants.
| Earth Masses | Jupiter Masses | Solar Masses |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Astronomy Time Units
Astronomers use the same time units as everyone else, from the very small nanoseconds, to seconds, minutes, hours, days and years. This is true with two exceptions known as sidereal days and sidereal years. These refer to time relative to the celestial objects (the fixed stars). The Earth rotates every 24 hours relative to the Sun. But we are moving in a circle around the Sun. In comparison, the Earth rotates every 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4.0905 seconds (23.9344696 hours) compared to the stars in the celestial sphere. This is known as a sidereal day.
In the same vein, a sidereal year is the time it takes the Earth to complete one orbit around the Sun relative to the celestial sphere. Where a year is 365 days, a sidereal year is 365.256363004 days, or 1,224.5 seconds more than a calendar year.
| Sidereal Day | Sidereal Year |
|---|---|
|
|