The Weight or Mass of an Ellipsoid calculator computes the weight or mass of an ellipsoid with semi-axes of lengths a, b, and c (see diagram), where the composition of the ellipsoid has a mean density (mD). 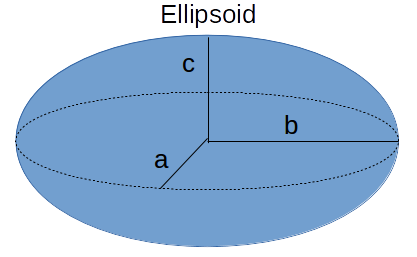
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (a) semi-axis of the ellipsoid.
- (b) semi-axis of the ellipsoid.
- (c) semi-axis of the ellipsoid.
- (mD) mean density of the sphere
Mass of Ellipsoid (m): The mass of the ellipsoid is returned in kilograms. However, this can be automatically converted to other mass and weight units (e.g. pounds, tons, grams) via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The formula for the mass or weight of an ellipsoid is:
`m =[4/3 * pi *a*b*c]*mD`
where:
- m = mass of the ellipsoid
- a = length of semi-axis a
- b = length of semi-axis b
- c = length of semi-axis c
- mD = mean density of composition
The formula computes the volume of the geometric shape based on the input parameters. With the computed volume, this formula then executes the simple equation below to compute the approximate mass of the object.
where:
- rho is the mean density
Ellipsoid Calculator
Ellipsoid - Volume computes the volume of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c)
- Ellipsoid - Surface Area computes the surface area of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c)
- Ellipsoid - Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c) and the mean density.
- Ellipsoid Cap - Volume computes the volume of a section of an ellipsoid.
- Oblate Spheroid - Volume computes the volume of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c)
- Oblate Spheroid- Surface Area computes the surface area of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c)
- Oblate Spheroid- Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c) and the mean density.
- Sphere - Volume computes the volume of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a)
- Sphere - Surface Area computes the surface area of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a)
- Sphere - Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a) and the mean density.
- Circular - Volume: Computes the volume of a column with a circular top and bottom and vertical sides.
- Circular - Mass: Computes the mass/weight of circular volume based on its dimensions and mean density.
- Elliptical Volume: Computes the volume of a column with an elliptical top and bottom and vertical sides.
- Elliptical - Mass: Computes the mass/weight of an elliptical volume based on its dimensions and mean density.
- Ellipse Vertical Chord from Edge (VE): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the edge.
- Ellipse Vertical Chord from Center (VC): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the center.
- Ellipse Horizontal Chord from Edge (HE): Computes the length of the horizontal chord of an ellipse based on distance from the edge.
- Ellipse Horizontal Chord from Center (HC): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the center.
- Common Mean Density: Provides a lookup function to find the mean density of hundreds of materials (woods, metals, liquids, chemicals, food items, soils, and more)
Mean Density Table
| Common Mean Densities in Kilograms per Meter Cubed (kg/m3) | ||
|
Fluids
Fuels
Market-Ready Grains |
Metals
|
Earthen
Synthetic
Organic
|
| Mean Density Lookup Function | ||
Mean density is scientifically volume divided by mass. There are various unit for density adopted by cultures and industries. Common units for density included the following:
- kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3)
- grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3)
- grams per liter (g/L)
- pounds per cubic feet (lb/ft3)
- ounces per cubic inch (oz/in3)
- pounds per barrel (lb/bbl)
- pounds per bushel (lb/bu)
If you want to identify a material by its density, use the Density Within Range tool.

Weight is technically the downward force that a mass exerts based on the force of gravity and the mass of the object. On the surface of the Earth, mass and weight are often interchanged. In some places, objects are sold by the gram (mass), and in other locations, the same objects are sold by the ounce (weight).
The Weight Calculators use the dimensions of an object and its shape to compute the objects volume. They then apply a density associated with a material to estimate the objects weight.
Weight Calculators
- Weight from Area, Height and Density
- Cube Weight
- Box Weight
- Cone Weight
- Cone Frustum Weight
- Cylinder Weight
- Slanted Cylinder Weight
- Semicircle Weight
- Triangular Weight
- Quadrilateral Weight
- Pentagon Weight
- Hexagon Weight
- Heptagon Weight
- Octagon Weight
- Nonagon Weight
- Decagon Weight
- Hendecagon Weight
- Dodecagon Weight
- Paraboloid Weight
- Polygon Pyramid Frustum Weight
- Sphere Mass
- Sphere Cap Weight
- Sphere Segment Weight
- Sphere Shell Mass
- Oblate Spheroid Mass
- Ellipsoid Weight
- Torus Weight
- Bottle Weight
- Bottle Content Weight
- Chamfer Weight
- Ring Weight