The Mass or Weight of an Oblate Spheroid calculator computes the volume of an oblate spheroid based on the semi-major(b) and semi- minor (c) axis with the assumption that the spheroid is generated via rotation around the minor axis (see diagram). 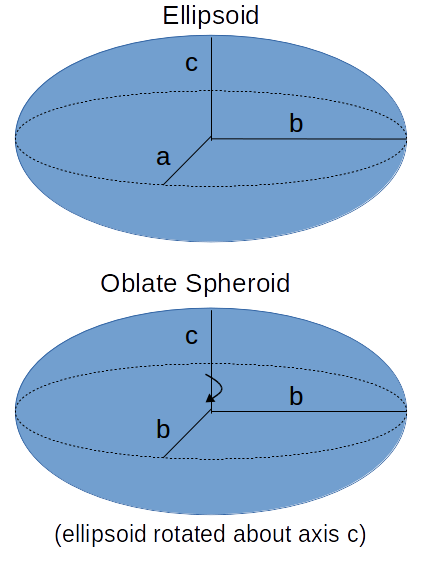
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose your length units for a and b (e.g. feet, meters, light-years), and enter the following:
- (b) - semi-major axis, the distance from the oblate spheroid's center along the longest axis of the spheroid
- (c) - semi-minor axis, the distance from the oblate spheroid's center along the shortest axis of the spheroid
- (mD) - the mean density of the substance comprising the oblate spheroid.
Oblate Spheroid Mass / Weight: The mass (M) is returned in kilograms. However, this can be automatically converted to other mass and weight units (e.g. tons, pounds) via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The oblate spheroid is an ellipsoid that can be formed by rotating an ellipse about its minor axis. The rotational axis thus formed will appear to be the oblate spheroid's polar axis. The oblate spheroid is fully described then by its semi-major and semi-minor axes.
One important shape in nature that is close to (though not exactly) an oblate spheroid is the Earth which has a semi-minor axis (c) which is the polar radius of 6,356 kilometers, and a semi-major axis (b) which is the equatorial radius of 6,378 kilometers. Consideration: what force would make the equatorial radius larger than the polar radius?
Ellipsoid Calculator
Ellipsoid - Volume computes the volume of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c)
- Ellipsoid - Surface Area computes the surface area of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c)
- Ellipsoid - Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c) and the mean density.
- Ellipsoid Cap - Volume computes the volume of a section of an ellipsoid.
- Oblate Spheroid - Volume computes the volume of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c)
- Oblate Spheroid- Surface Area computes the surface area of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c)
- Oblate Spheroid- Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c) and the mean density.
- Sphere - Volume computes the volume of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a)
- Sphere - Surface Area computes the surface area of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a)
- Sphere - Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a) and the mean density.
- Circular - Volume: Computes the volume of a column with a circular top and bottom and vertical sides.
- Circular - Mass: Computes the mass/weight of circular volume based on its dimensions and mean density.
- Elliptical Volume: Computes the volume of a column with an elliptical top and bottom and vertical sides.
- Elliptical - Mass: Computes the mass/weight of an elliptical volume based on its dimensions and mean density.
- Ellipse Vertical Chord from Edge (VE): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the edge.
- Ellipse Vertical Chord from Center (VC): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the center.
- Ellipse Horizontal Chord from Edge (HE): Computes the length of the horizontal chord of an ellipse based on distance from the edge.
- Ellipse Horizontal Chord from Center (HC): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the center.
- Common Mean Density: Provides a lookup function to find the mean density of hundreds of materials (woods, metals, liquids, chemicals, food items, soils, and more)
|
Metals Densities
|
Metals are materials characterized by its physical and chemical properties, primarily its ability to conduct electricity and heat, its luster or shine when polished, its malleability (ability to be hammered or pressed into shapes), and its ductility (ability to be drawn into wires). Metals typically have a crystalline structure and are found naturally in solid form (with the exception of mercury, which is a liquid at room temperature).
Metals make up a large portion of the periodic table of elements, with examples including iron, copper, gold, silver, aluminum, and titanium, among many others. Metals are essential in various industries such as construction, manufacturing, electronics, transportation, and energy production due to their unique properties and versatility.
Metals are generally dense materials. Density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume. Metals tend to have high densities because their atoms are closely packed together in a crystalline structure. This close packing of atoms contributes to their characteristic properties such as strength, malleability, and conductivity.
However, it's important to note that the density of metals can vary widely depending on factors such as their elemental composition, crystal structure, and any impurities present. For example, some metals like lead and platinum are denser than others like aluminum or magnesium.
Related Calculators
The following table contains links to calculators that compute the volume of other shapes:
| Other Volume Calculators | |||
| Various Shapes | Polygon Columns | ||
| Cube | Triangular Prism | Triangular | |
| Box | Paraboloid | Quadrilateral | |
| Cone | Polygon based Pyramid | Pentagon | |
| Cone Frustum | Pyramid Frustum | Hexagon | |
| Cylinder | Sphere | Heptagon | |
| Slanted Cylinder | Sphere Cap | Octagon | |
| Ellipsoid | Oblate Spheroid | Nonagon | |
| Torus | Capsule | Decagon | |
