The Mean Arterial Press calculator compute the mean arterial pressure and pulse pressure based on the diastolic pressure and the systolic pressure.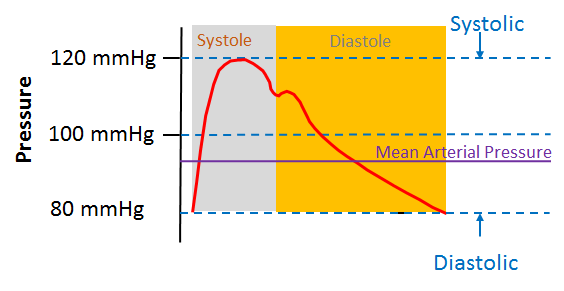
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (DP) Diastolic Blood Pressure
- (SP) Systolic Blood Pressure
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP): The mean arterial pressure and pulse pressure are returned in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). However, these can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) is a term used in medicine to describe an average blood pressure in an individual. It is defined as the average arterial pressure during a single cardiac cycle.
`MAP = DP+(SP -DP)/3`
Where:
- MAP = Mean Arterial Pressure
- DP = Diastolic Blood Pressure
- SP = Systolic Blood Pressure
Example: If BP = 120/80 mmHg
`MAP=80+1/3(120−80) = 80+13.3=93.3 mmHg`
The formula for Pulse Pressure is:
`PP = SP - BP`
- PP = Pulse Pressure
- DP = Diastolic Blood Pressure
- SP = Systolic Blood Pressure
MAP is considered to be the perfusion pressure seen by organs in the body. It is believed that a MAP that is greater than 60 mmHg is enough to sustain the organs of the average person. MAP is normally between 70 to 110 mmHg If the MAP falls below this number for an appreciable time, vital organs will not get enough Oxygen perfusion, and will become ischemic.
he normal range for Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) is 70–100 mmHg (typically considered normal and adequate for organ perfusion)
Key Thresholds:
- MAP > 60 mmHg → Minimum required to perfuse vital organs (brain, kidneys, heart)
- MAP < 60 mmHg → Can indicate shock, organ hypoperfusion, or circulatory failure
- MAP > 100 mmHg → May suggest hypertension, increased cardiac workload, or risk of vascular damage
Heart, Cardiology and Blood Calculators
- Cardiac Stroke Volume: Computes the volume blood pumped in one stroke based on the end diastolic and systolic volumes.
- Cardiac Output: Computes the output of a heart based on the heart rate, end diastolic volume and the end systolic volume.
- Cardiac Output with Stroke Volume: Computes the volume rate of blood pumped by the heart in one minute based on the beats per minute and the stroke volume.
- Ejection Fraction: Computes the Ejection Fraction percentage based on the end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes.
- Heart Stroke Work: Computes the amount of work performed by the heart during a single heartbeat to pump blood based on the Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) and Stroke Volume(SV).
- Mean Arterial Press: Compute the mean arterial pressure and pulse pressure based on the diastolic pressure and the systolic pressure.
- Cardiac Stroke Work: Computes work done by the ventricle to eject a volume of blood into the aorta based on the afterload pressure, stroke volume, blood stroke mass and blood flow velocity.
- Cardiac Flow (Q): Computes the flow factor of an artery based on the diameter and blood flow velocity.
- Body Surface Area (BSA): Wide range of calculators in one function to compute the body surface area base on one of many common methods (e.g., Mosteller, Takahira)
- Hagen-Poiseuille Resistance: Fluid resistance of blood and plasma based on viscosity, length and radius of vessel.
- Poiseuille's Law: Fluid flow rate from change in pressure, length, diameter and viscosity
- Poiseuille's Velocity of Compressible Fluids: Fluid velocity based on tube radius and length, input and output pressures, and fluid viscosity.
- Heart Chamber Pressure via the Law of Laplace: Pressure on membrane wall based on wall stress, chamber radius and vascular wall thickness.
- Heart Wall Stress via the Law of Laplace: Stress on the membrane wall of based on the blood pressure, radius of the chamber (r) and the vascular wall thickness (T).
- Blood Flow Rate using Darcy's Law: Blood flow through a vessel based on a change in pressure and a resistance factor.
- Change in Vascular Pressure: Change in pressure at two points in a vessel.
- Blood Pressure: Blood pressure based on Cardiac Output and Blood Flow Resistance
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP): Calculates MAP from Pulse Pressure and Diastolic Pressure
- Mean Arterial Pressure and Pulse Pressure: Calculates MAP and Pulse Pressure from Diastolic Pressure and Systolic Blood Pressure
- Cardiac Output from Heart Rate and Stroke Volume: Output of a heart based on the heart stroke volume and the heart rate.
