The Hagen-Poiseuille Resistance calculator computes the fluid resistance in a blood vessel or small tube based on the viscosity (η) and length (L) and radius (r) of the vessel.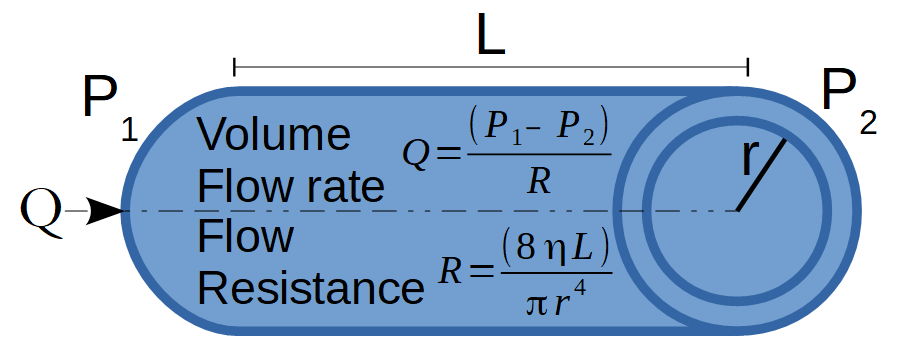
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (η) Fluid Viscosity (Default: 0.04 poise for blood at 37° C)
- (L) Length of Vessel
- (r) Inner Radius of Vessel
Tube/Vessel Resistance (R): The calculator returns the resistance in mmHg•min / L.
The Math / Science
Poiseuille's Law relates the fluid resistance of blood flow through a small blood vessel with the blood vessel's radius (r), the length (λ) of the artery, and the viscosity (η) of the blood. The formula for Poiseuille's Law of Blood Resistance is:
` R = (8•η•λ) / (π•r^4)`
where:
- R is the Blood Flow Resistance
- η is the viscosity
- λ is the length of the blood vessel or artery
- r is the interior radius of the blood vessel or artery
The volume of a homogeneous fluid passing per unit time through a capillary tube without turbulence is proportional to the pressure difference between its ends and is proportional to the fourth power of its internal radius.
The volumetric flow rate is also inversely proportional to the length of the tube and the viscosity of the fluid. This formula applies to the flow of blood in an artery because we can treat the blood flow as a laminar flow of a uniformly viscous liquid.
Viscosity of Blood
The viscosity of blood refers to its resistance to flow and is an important factor in circulatory dynamics.
Typical Viscosity Values:
- Whole blood viscosity: ~3 to 4 centipoise (cP) at 37°C under normal shear rates (Water, for comparison, has a viscosity of about 0.7–1.0 cP at the same temperature.)
- Plasma viscosity: ~1.1 to 1.3 cP at 37°C
Note: Viscosity can vary depending on factors like:
- Hematocrit (the proportion of red blood cells)
- Temperature
- Shear rate (blood is a non-Newtonian fluid, so its viscosity changes with flow conditions)
- Diseases (e.g., polycythemia increases viscosity, anemia decreases it)
Heart, Cardiology and Blood Calculators
- Cardiac Stroke Volume: Computes the volume blood pumped in one stroke based on the end diastolic and systolic volumes.
- Cardiac Output: Computes the output of a heart based on the heart rate, end diastolic volume and the end systolic volume.
- Cardiac Output with Stroke Volume: Computes the volume rate of blood pumped by the heart in one minute based on the beats per minute and the stroke volume.
- Ejection Fraction: Computes the Ejection Fraction percentage based on the end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes.
- Heart Stroke Work: Computes the amount of work performed by the heart during a single heartbeat to pump blood based on the Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) and Stroke Volume(SV).
- Mean Arterial Press: Compute the mean arterial pressure and pulse pressure based on the diastolic pressure and the systolic pressure.
- Cardiac Stroke Work: Computes work done by the ventricle to eject a volume of blood into the aorta based on the afterload pressure, stroke volume, blood stroke mass and blood flow velocity.
- Cardiac Flow (Q): Computes the flow factor of an artery based on the diameter and blood flow velocity.
- Body Surface Area (BSA): Wide range of calculators in one function to compute the body surface area base on one of many common methods (e.g., Mosteller, Takahira)
- Hagen-Poiseuille Resistance: Fluid resistance of blood and plasma based on viscosity, length and radius of vessel.
- Poiseuille's Law: Fluid flow rate from change in pressure, length, diameter and viscosity
- Poiseuille's Velocity of Compressible Fluids: Fluid velocity based on tube radius and length, input and output pressures, and fluid viscosity.
- Heart Chamber Pressure via the Law of Laplace: Pressure on membrane wall based on wall stress, chamber radius and vascular wall thickness.
- Heart Wall Stress via the Law of Laplace: Stress on the membrane wall of based on the blood pressure, radius of the chamber (r) and the vascular wall thickness (T).
- Blood Flow Rate using Darcy's Law: Blood flow through a vessel based on a change in pressure and a resistance factor.
- Change in Vascular Pressure: Change in pressure at two points in a vessel.
- Blood Pressure: Blood pressure based on Cardiac Output and Blood Flow Resistance
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP): Calculates MAP from Pulse Pressure and Diastolic Pressure
- Mean Arterial Pressure and Pulse Pressure: Calculates MAP and Pulse Pressure from Diastolic Pressure and Systolic Blood Pressure
- Cardiac Output from Heart Rate and Stroke Volume: Output of a heart based on the heart stroke volume and the heart rate.
