The Ghyben-Herzberg Relation (Saltwater Intrusion) calculator computes the depth of fresh water in an aquifer below sea level (z) based on the depth of fresh water above sea level (h).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (h) Depth or thickness of Freshwater zone above sea level
- (ρf) Density of Freshwater (1.000 g/cm3)
- (ρs) Density of Saltwater (1.025 g/cm3)
Depth of Fresh Water below Sea Level (z): The calculator returns the depth (z) in feet. However, this can be automatically converted to other length units via the pull-down menu.
The Science
The Ghyben-Herzberg Relation (Saltwater Intrusion) ratio states that for every foot of fresh water in an unconfined aquifer above sea level, there will be forty feet of fresh water in the aquifer below sea level. The formula for the depth of fresh water below sea level is: 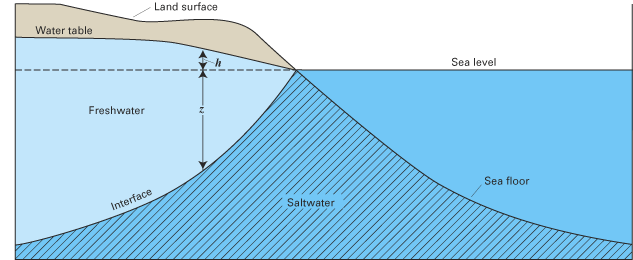
z=ρf /(ρs - ρf) • h
where:
- z = depth of fresh water below sea level
- h = thickness of the freshwater zone above sea level
- ρf = density of freshwater (1.000 g/cm3)
- ρs = density of saltwater (1.025 g/cm3)
Saltwater Intrusion is the movement of saline water in freshwater aquifers, which can lead to contamination of drinking sources and other consequences. Saltwater intrusion occurs naturally to some degree in most coastal aquifers, owing to they hydraulic connection between groundwater and seawater. Because saltwater has a higher mineral content than freshwater, it is denser and a higher water pressure. As a result, saltwater can push inland beneath freshwater. Certain human activities, especially groundwater pumping from coastal freshwater wells, have increased saltwater intrusion in many coastal areas. Water extraction drops the level of fresh groundwater, reducing its water pressure and allowing saltwater to flow further inland. Other contributors to saltwater intrusion include navigation channels or agricultural and drainage channels, which provide conduits for saltwater to move inland, and sea level rise. Saltwater intrusion can also be worsened by extreme events like hurricane storm surges.
Water Related Calculators
- Underwater Pressure: Computes the added pressure exerted underwater by the water column directly overhead as a function of the density of the water, depth under water, and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Pore Water Pressure: Measure of the pressure of groundwater held within a soil or rock, in gaps between particles (pores), relative to atmospheric pressure.
- Osmotic Pressure: Computes the osmotic pressure based on the molar concentration of the solution (M), the temperature (T) and the Ideal Gas Constant (R).
- Density of water at STP: 998.2071 kg / m3
- Density of Deawater: 1,025 kg / m3
- Saltwater Intrusion: Uses the Ghyben-Herzberg Relation to compute the depth of fresh water in an aquifer below sea leve based on the depth of fresh water above sea level.
- Snow or Water Density: Returns the kilograms per meters cubed (kg/m3) for snow of different types or water at different temperatures per the US Geological Survey (USGS).
- Water Density by Temperature: Computes the density of water as a function of temperature, using the standard density of water (ρ) at standard temperature and pressure, and the unique temperature expansion coefficient of water.
- Pressure to Water Depth: Computes approximated depth of water where the pressure would occur.
- Bernoulli's Equation (Pressure): Uses Bernoulli's equation to compute fluid pressure (p1) based on the fluid velocities, heights and second pressure (p2).
- Bernoulli's Equation (Velocity): Uses Bernoulli's equation to compute fluid velocity (v1) based on the pressures, heights and second velocity (v2).
- Bernoulli's Equation (Elevation): Uses Bernoulli's equation to compute elevation (h1) based on the pressures, fluid velocitities and second height (h2)
- Volume of Water in a Well: Compute the volume of water in a well based on the static water level and the diameter of the well pipe..
- Pressure to Water Depth: Computes the height needed to acheive a desired pressure considering the density of liquid (e.g., water).
- Pressure Head: Computes the pressure based on the height of Gravity-Fed water from a tank or resevoir.
- Underwater Pressure: Computes the added pressure exerted underwater by the water column directly overhead as a function of the density of the water, depth under water, and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Heat Load and Water Flow: Computes the ton of heat capacity associated with a volumetric flow of water and a change in temperature.
References
Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saltwater_intrusion#Ghyben-Herzberg_relation)
