Processing...
` = Delta(vec( alpha ^o & "AS" ) , vec( beta ^o & "WS" ))`
Enter a value for all fields
The Flight Navigation Correction Angle calculator computes the navigation angle/azimuth correction angle (Δ) using the wind speed (WS), wind direction (β), Flight Heading (α) and an Air Speed (AS).
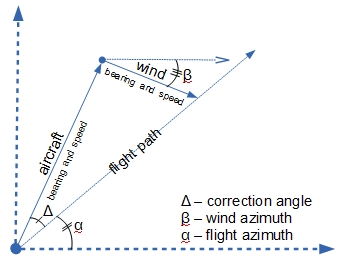 Correction angle parameters
Correction angle parameters
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (α) Flight Angle(azimuth)
- (AS) Air Speed
- (WS) Wind Speed
- (β) Wind Direction
Navigation Correction Angle (Δ): The calculator returns the angle in degrees. However this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
Flight and Navigation Calculators
- Correction Angle: Computes the navigation angle/azimuth correction angle using the wind speed, wind direction, flight heading and an Air Speed.
- Ground Speed: Computes the ground speed based on the wind speed, wind direction, a Flight Heading and an Air Speed.
- Haversine - Distance: Computes the distance between two points on a spherical model of the Earth along a great circle arc. This also includes the rhumb line distance and azimuth for the rhumb line.
- Travel Time between Coordinates: Computes the time to travel between to points on the globe in a great circle arc at an average velocity.
- Distance to Sea Level Horizon at Altitude: Computes the distance to the horizon from a specified height using a spherical model the mean spherical radius of the Earth
- Force of Drag: Calculates the resisting force of drag on an object flowing through a medium (e.g. air).
- Force of Lift: Computes the lifting force on the surface area of a wing based on the wing surface area, air flow velocity, density of air and a lift coefficient.
- Lift Coefficient: Compute the lift coefficient of a wing based on lift force, wing surface area, wind speed and density of air.
- Velocity Needed for Takeoff: Computes the velocity required to create more lift than the weight of an aircraft or watercraft using a wing (e.g. hydrofoil).
- Glide Ratio: Computes the glide ratio based on the change in forward distance and the change in altitude.
- Wing Surface Area: Computes the wing surface area required to achieve lift, base on a lift coefficient, lift force, wind speed and density of air.
- Velocity of Air over the Wing: Computes the velocity required to achieve a lift, based on lift coefficient, lift force, wing surface area and density of air.
- Air Speed from Pressures: It uses the Bernoulli Equation to estimate air speed based on the total Pressure measured by a pilot tube, total Static local atmospheric pressure and the Density of Air.
- Center of Mass: Computes the vehicle center of mass between two loads (masses).
- Cloud Base: Estimates the height above the ground of the cloud base from the Dew Point and Surface Temperature.
Sailing and Navigation Calculators:
Bruce Number: Computes the ratio of the square root of sail area to the cube root of displacement of a sail boat
- Sail Area / Displacement Ratio: Compute SA/D ratio for sail boats.
- Displacement-Length Ratio: Computes a metric to describe how heavy a boat is in relation to its waterline.
- Capsize Screening Formula: Computes a metric to describe a boat's stability in rough seas.
- Vessel Displacement Volume: Computes the cubic feet displacement associated with the weight displacement.
- Weight of Seawater: Computes the weight and mass of a volume of seawater.
- Time to Sink: Compute the time it takes for a breach (water in) to surpass the displacement of the boat.
- Haversine Distance (decimal degrees): Compute the Distance Between two Points on the Earth (Great Circle Arc)
- Haversine Distance (Degrees, Minutes and Seconds): Compute the Distance Between two Points on a Sphere (Great Circle Arc) using degrees, minutes and seconds verses decimal degrees.
- Rhumb Line Azimuth: Computes the azimuth heading one can navigate for a path that crosses all meridians of longitude at a constant angle.
- Rhumb Line Distance: Computes the distance traveled between two points on the globe if traveled via a rhumb line.
- Correction Angle:
navigation equation that compensates for air or water currents.
- Decimal Degrees: Compute decimal degree angles from degrees, minutes and seconds,[CLICK HERE].
- Nautical Travel Cost: Computes the total cost to travel a distance based on the cost rate and distance traveled.
- Travel Time between Coordinates: Compute the time to travel between two location (latitudes and longitudes) based on a average speed
- Distance to Sea Level Horizon: Computes the distance to the horizon from a specified height using a spherical model the mean spherical radius of the Earth
The Math / Science
The Navigation Correction Angle formula calculate the course correction angle needed to compensate for wind of a certain bearing and at a certain velocity in order to continue at the desired heading. This is done with vector arithmetic.
