The Greenhouse Calculator provides useful equations and data for people who work with greenhouses and high-tunnels. This includes basics for greenhouse construction and heating, for mulching and coverage with straw and for greenhouse planters. DIFFERENT GREENHOUSE SHAPES.png) Gabled Roof Structure
Gabled Roof Structure.png) Arched Roofed Structure
Arched Roofed Structure.png) Quonset Hut
Quonset Hut
Greenhouse or High-tunnel Volume and Surface Area calculators include (see diagram):
- Volume of a Gabled Greenhouse: Enter the dimensions of a gabled building and compute the cubic feet volume.
- Volume of an Arched Roofed Greenhouse: Enter the dimensions of an arched roofed building (see diagram) and compute the cubic feet volume.
- Volume of a Quonset Hut Greenhouse: Enter the dimensions of the Quonset Hut and compute the cubic feet volume.
- Surface Area of a Gabled Greenhouse: Enter the dimensions of a normal gabled building and compute the square feet surface area.
- Surface Area of an Arched Roof Greenhouse: Enter the dimensions of an arched roof building and compute the square feet surface area.
- Surface Area of a Quonset Hut Greenhouse: Enter the dimensions of a Quonset Hut and compute the square feet surface area.
- Conductive Heat Loss: Enter the surface area, the heat loss coefficient for the surface material and the maximum heat range, and the calculator will compute the BTUs per hour needed to heat the inside. (See Heating a Greenhouse below)
- Greenhouse Airflow Metrics: Computes airflow and Evaporative Cooling Efficiency
To compute the amount of mulch or straw needed for ground cover in your greenhouse, use the Mulching Calculator (Click HERE)
To compute the amount of soil and water needed for elevated planters in your greenhouse, use the Planter Calculator (Click HERE).
Greenhouse Buildings
The figure shows three styles (building shapes) of greenhouses. 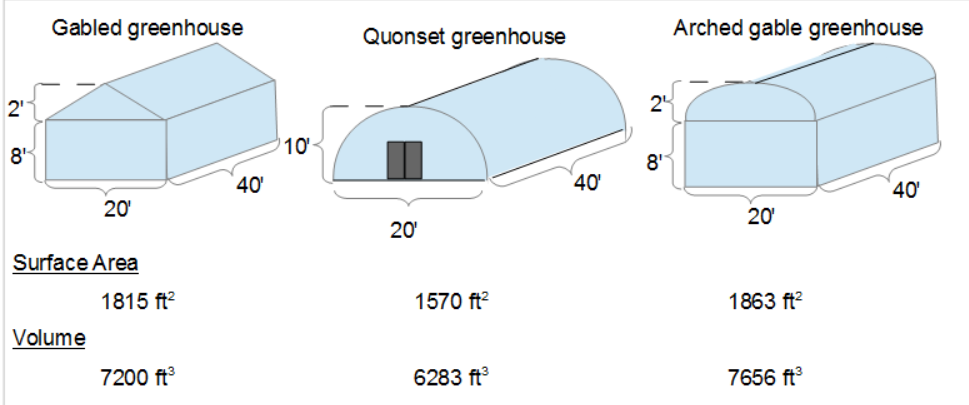 Greenhouse shape vs volume and surface area comparison It also shows a comparison of the surface area and volume for three greenhouses with the same footprint (20' wide, 40' length, 10' high). The surface area and volume of the greenhouses are useful for heating, cooling and humidity monitoring. The surface area is also useful in calculating the material needs for the construction of greenhouses. The building equations include calculations for the volume and surface area for three types (building shapes) of greenhouses:
Greenhouse shape vs volume and surface area comparison It also shows a comparison of the surface area and volume for three greenhouses with the same footprint (20' wide, 40' length, 10' high). The surface area and volume of the greenhouses are useful for heating, cooling and humidity monitoring. The surface area is also useful in calculating the material needs for the construction of greenhouses. The building equations include calculations for the volume and surface area for three types (building shapes) of greenhouses:
- Standard greenhouse with a gabled roof
- Greenhouse with an arched roof
- Quonset style greenhouse
The calculator also includes an equation for the greenhouse's conductive heat loss through the outer skin based on the Surface Area, material insulating factor (U), and the maximum temperature variance.
vCalc provides automatic unit conversions for both input parameters and output results that included English and Metric (SI) units.
Heating a greenhouse
The primary use of a greenhouse is to create an environment conducive to growing plants with natural light, but where the temperature and humidity is controlled by the gardener. The basic greenhouse employs a substantial amount of passive solar heating. However, this may not be enough in some circumstances to prevent freezing or to reach maximum conditions for the growth of some plants. In these circumstances, greenhouses are often constructed with supplemental heating. The primary heat loss for a greenhouse are conductive heat loss through the greenhouse material and through air exchange with the outdoors through openings (even very small ones).
Conductive Heat Loss
Conductive heat loss is the transfer of heat through a membrane. For greenhouses, the transfer of concern is typically warmth from within the greenhouse that is lost through the skin of the greenhouse into the outside environment. The equation for the conductive heat loss is relatively simple:
CHL = A • vT • U
Where:
- CHL is Conductive Heat Loss
- A is the surface area
- vT is the maximum temperature variance (indoor to outdoor)
- U is the insulating coefficient.
The U value is published for many material. Consult your product supplier for the actual U value of the material planned to be used. However, some common U values are as follows:
- 0.15 for high performance triple pained glass
- 0.3 to 0.5 for good double pained glass
- 0.7 double layered plastic
- 1.22 for single paned glazed glass
Note: U is the reciprocal of R
Consider the extreme cases in your area for the maximum temperature variance. For example, if your plants require a minimum of 57oF, and the possible low temperature outside is -14oF, the variance is 71oF.
The result of the equation is BTU/hour required to compensate for the conductive heat loss.
Potting Mix and Garden Soil
Potting Mix is combination of organic materials (e.g., peat moss, aged bark and pumice) but no soil (dirt) that is used in lieu of potting soil to improve drainage. Because potting mix has no soil, it tends to be lighter than potting soil and provides a more sterile medium for plants with fewer disease carrying agents. Potting mix is most commonly recommended for plants in containers, and potting mix is particularly desirable for starting seeds. Garden Soil is a gardening product sold that contains natural soil (dirt) comprised of mixture of loam, clay and sand. Garden soil is often used in raised gardens or planters as a healthy and easy medium for plants and seeds on top of the natural soil in one's yard. Garden Soil differs from Potting Mix in that garden soil contains real soil (dirt), where Potting Mix does not.
Potting Mix and Garden Soil Price Survey
vCalc conducts a periodic pricing survey from nationally advertised retailers for various materials. The current Garden Soil Price Survey sample information for Garden Soil and Potting Mix is as follows:
- Date: 5/14/24
- Store: Menards
- Garden Soil (1 ft3): $6.49
- Garden Soil (1.5 ft3): $7.49
- Garden Soil (2 ft3): $9.99
- Potting Mix (1.25 ft3): $13.71
- Potting Mix (2.5 ft3): $27.43
Always use local pricing! There is NO implied guarantee that these prices are available in your area or that products will be available. This pricing is purely provided for estimation convenience.
See Also
- HouseBuilder - Construction calculator for stick-build and masonry buildings and sheds.
- Sandbox Calculator - Computes how many bags of play sand you need for different shaped sandboxes.
