Instructions
This equations solves a system of equations. The equations are entered as strings in the Dataset System of Linear Equations. You can enter as
many equations as you want, but your system should have the same number of equations as unknowns (variables). Equations are entered similar to way they would be written on paper, e.g. "3x + 2y - 10 = z + 5". The syntax of equations allow only the addition (+) and subtraction (-) operators. Variables could be any name not just single letters, e.g: "3tomatoes + 2carrots - 10 = -onions + 5". However they must contain only letters, underscores or digits and may not begin with a digit.
About the algorithm
The algorithm uses the Gaussian elimination method to solve the equation.
To perform Gaussian elimination, the coefficients of the terms in the system of linear equations are used to create a type of matrix called an augmented matrix.
Then, elementary row operations are used to simplify the matrix. The three types of row operations used are:
Type 1: Switching one row with another row.
Type 2: Multiplying a row by a non-zero number.
Type 3: Adding or subtracting a row from another row.
The goal of Gaussian elimination is to get the matrix in row-echelon form. If a matrix is in row-echelon form, that means that reading from left to right, each row will start with at least one more zero term than the row above it.
For example, the following matrix is in row echelon form, and its leading coefficients are shown in red.
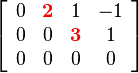
It is in echelon form because the zero row is at the bottom, and the leading coefficient of the second row (in the third column), is to the right of the leading coefficient of the first row (in the second column).
We will use Gaussian Elimination to solve the linear system:
X1 + 2X2 + 3X3 = 9
2X1 - X2 + X3 = 8
3X1 - X3 = 3
The augmented matrix is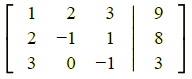
The Gaussian Elimination algorithm proceeds as follows:
We have brought the matrix to row-echelon form. The corresponding system
X1 + 2X2 + 3X3 = 9
X2 + X3 = 3
X3 = 3
is easily solved from the bottom up:
X3 = 3
X2 + 3 = 2 -> X2 = -1
X1 + 2(-1) + 3(3) = 9 -> X1 = 2
Thus, the solution of the original system is X1 = 2 , X2 = -1 , X3 = 3
REFERENCES:
HMC Mathematics Online Tutorial
Wikipedia