Processing...
A nail is a small, slender metal fastener used to join materials together, typically wood. Nails are driven into surfaces using a hammer or a nail gun and hold materials in place through friction and compression.
Nail Parts:
- Head – The flat or shaped top that prevents the nail from going all the way through the material.
- Shank – The long, thin body that penetrates the material; it may be smooth, ringed, or twisted for better grip.
- Point – The sharp end that helps the nail pierce the surface.
Nail Types:
- Common Nails – General-purpose nails for construction.
- Finishing Nails – Have small heads for a clean appearance, often used in trim work.
- Framing Nails – Heavy-duty nails for structural work.
- Roofing Nails – Large-headed nails for securing shingles.
- Cut Nails and Masonry Nails - Extra hard nails use for hard surfaces such as concrete and solid wood.
- Flooring Nails - Slender nails used in a nail gun or driver for hardwood flooring.
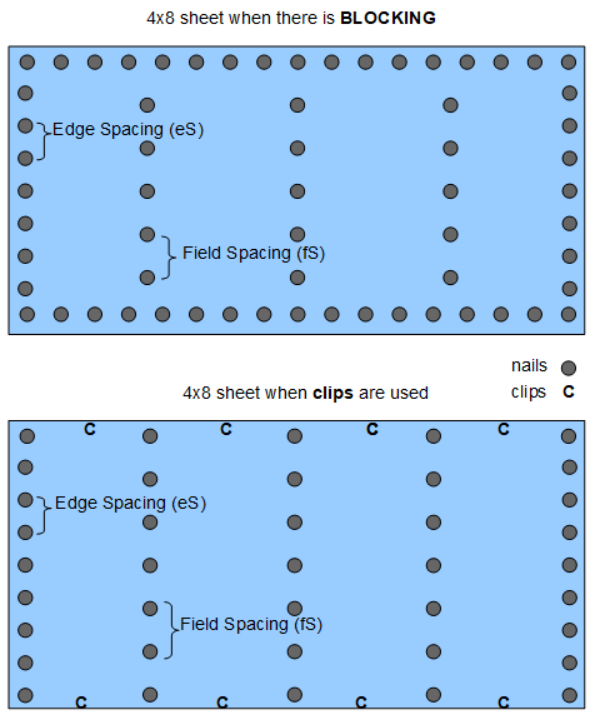
The diagram (above right) shows the patern for nails on 4x8 sheathing on a roof structure (rafters or trusses).