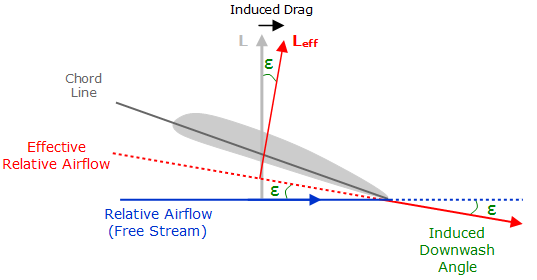
Calculation of Induced Drag
For a planar wing wing with an elliptical lift distribution, induced drag is often calculated as follows. These equations make the induced drag depend on the square of the lift, for a given aspect ratio and surface area (while varying the angle of attack), but as the accompanying graph shows, this is only an approximation and is not valid at high angles of attack (and probably not for very high values of aspect ratio either).
The following Equation computes Induced drag with (L)
D_i =L^2/(1/2*ρ_0*V_e^2*S*π*e*AR
Where:-
AR = the aspect ratio,
C_Di = induced drag coefficient (see Lifting-line theory),
C_L = is the lift coefficient,
D_i = is the induced drag,
e = is the wing span efficiency value by which the induced drag exceeds that of an elliptical lift distribution, typically 0.85 to 0.95,
L = is the lift,
S = is the gross wing area: the product of the wing span and the Mean Aerodynamic Chord.[1]
V = is the true airspeed,
V_e = is the equivalent airspeed,
ρ =is the air density and
ρ_0 = is 1.225 kg/m³, the air density at sea level, ISA conditions.