The Ballistic Range - Delta Height formula the difference in range of flight that should occur when objects are launched with the same initial velocity and launch angle but at two different heights above the plane.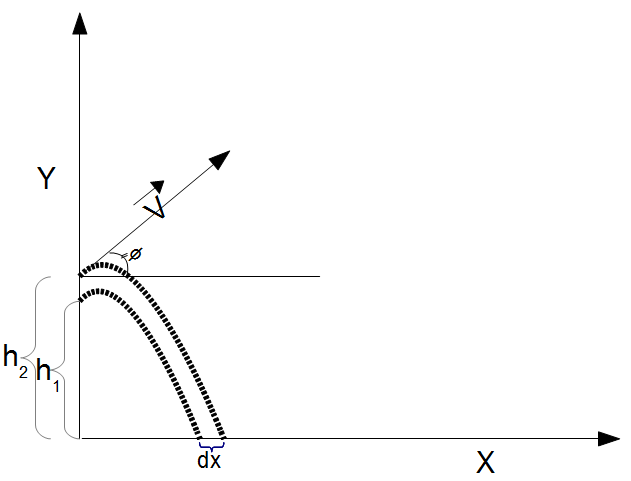 Ballistic Flight
Ballistic Flight
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (h1) Initial Height above the plane
- (Δh) Height Adjustment (plus or minus change in elevation)
- (θ) Launch Angle
- (V) Initial Velocity
- (g) Downward Acceleration due to Gravity
Change in Ballistic Range (dx): The change in range is returned in meters. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
This equation simply provided the difference in range based upon changing the elevation (height) of the initial launch point. It could tell you how much further or nearer your object will go out in the plane if the launch point is raised or lowered.
History and the High Ground
Historically, the high ground has been coveted on the battle field, because of the principle demonstrated in this equation. If the elevation is higher for one combatant, their munitions have a longer effective range, and their rocks, arrows, bombs or missiles will reach the enemy before the enemy's reaches them. This is why the high ground is sought on the battlefield and why defensive positions (e.g. castles) are typically placed on high ground such as mountain tops.
Firearm Calculators
- Sectional Density: Computes the factor used in the computation of the ballistic coefficient called sectional density.
- Bullet Ballistic Coefficient: Computes factor that represents a bullet's ability to overcome air resistance in flight.
- Ballistic Coefficient from Bullet's Mass, Diameter and Form Factor: Estimates the ballistic coefficient from the mass, diameter and form factor
- Miller Twist Rule: Computes the optimal barrel twist rate for stabilizing a bullet's flight given the bullet's diameter, length and mass.
- Taylor Knock-out Factor: Calculates a factor indicating the power of a round,.
- Greenhill Formula for Optimal Rifling Twist Rate: calculate the optimal barrel twist rate for stabilizing a bullet's flight given the bullet's diameter, length, specific gravity and velocity.
- Bullet Flight Range: Computes the maximum range (horizontal distance) traveled by a bullet based on the muzzle velocity, elevation angle and shooter height.
- Muzzle Energy of a Projectile: Calculates the kinetic energy in a bullet immediately after leaving the barrel given the bullet's mass and velocity.
- Recoil Velocity of a Gun: Computes the velocity at which a gun will move in the opposite direction in relation to the projectile that it fired.
- Cost per Round: Computes cost per round of ammunition based on the cost of a container of cartridges and the number of rounds in the container.
Rifle Sight Correction Angles: Computes the Minutes of Angle corrections for rifle sights.
- Shotgun Shell Reloading Cost: Computes the cost to reload used shotgun shells (hulls) with powder, shot, wads and primers.
- Shotgun Shell Loading Cost: Computes the cost to load new pre-primed shells (hulls) with power, shot and wads.
- Metal Ball Weight: Computes the mass (weight) of a spherical metal (e.g., steel) ball based on the size (diameter).
- Metal Cylinder Weight: Computes the mass (weight) of a metal cylinder based on the size (diameter and length).
